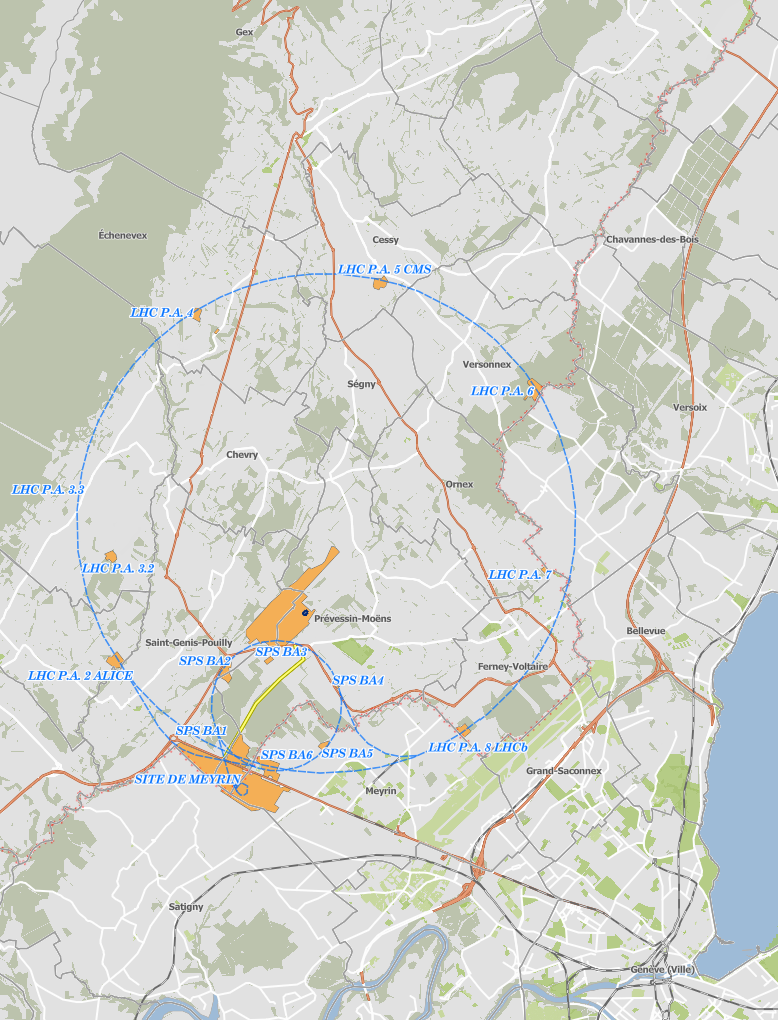
The access points to the LHC tunnel (the previous LEP tunnel) are numbered from 1 to 8. Point 1 (next to the main CERN site in Meyrin) houses the ATLAS experiment, Point 2 the Alice experiment, Point 8 the LHCb experiment, and Point 5 (in the far north of the ring near the village of Cessy) the CMS experiment. The other points house other services for the LHC: for instance Point 4 is where the beams receive a little accelerating push at every of their 11'000 passages per second, while Point 6 is where the LHC proton beams, which carry an enormous amount of energy, can be safely disposed of in the “beam dump”.
Point 5 is visible from far in the countryside because of its main high building in which the CMS detector was constructed, with a diameter of 15m and a length of about 25m. After a lot of testing of the CMS detector in the surface hall, the detector was lowered underground in pieces by a huge crane through a large access shaft. The central piece with the undivisible magnet was the heaviest, about 2000 tons, to lower 100m down.
On the site at Point 5 you will also find many other buildings housing services for the CMS experiment. Of note are the control room and the on-site computing resources for the so-called “High-Level Trigger”, a system that makes sure the dataflow is reduced to a managable level for the subsequent computing services – only 0.003% of the collisions is selected to be kept.
Below you find an overview map with the full LHC ring and the surrounding region, from Geneva with the Rhone river in the south, to the village of Gex at the feet of the Jura mountains in the north. The gray line with red hatching is the border between France and Switzerland.
