Speaker
Raymond Veness
(CERN)
Description
The LHC beam dump entrance window consists of a carbon-carbon composite structural sheet backed by a thin stainless steel foil for leak tightness.
The design of this window has highlighted issues that merit further investigation.
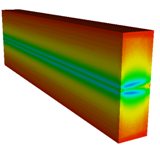
The use of the bulk coefficient of thermal expansion coefficient for the composite should be questioned
where there is a significant temperature gradient between individual fibres.
Differential thermal expansion between fibre and matrix could lead to thermally induced fatigue.
The validity of the analytical dynamic stress model used should be confirmed by finite element or experiment.
After a brief description of the window design, I will outline the issues. From this I will draw some conclusions
about further analysis and the possible advantages of using windows to perform material and structural experiments.
Primary author
Raymond Veness
(CERN)